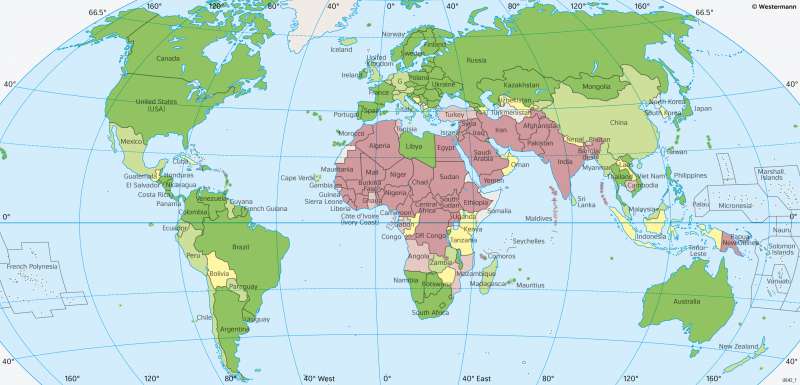
The World - Discrimination of women according to the Gender Development Index (GDI)
Level of development
978-3-14-100890-6 | Page 34 | Ill. 2
Overview
For measuring the discrimination against women, the Gender Development Index is an addition to the Human Development Index (HDI), that shows the way the living conditions for women and men are different in a country. To calculate the GDI, the HDI for women is divided by the HDI for men. Thus, a value below 1 means that women have worse living conditions and are discriminated. A value of 1 means that both men and women have the same living conditions.
The global range of GDI values is similar to that of the HDI, with values starting as low as 0.425. Due to the calculation, the GDI can reach above 1. Russia, for example, has the highest GDI with 1.007.
GDI values and their classification
In general, the GDI shows a clear spatial pattern. Countries with very high to high discrimination (0.425 to 0.925) are found in a belt between Central Africa, North Africa, South-west Asia and South Asia. The living situation of women is extremely difficult in countries with low GDI and low HDI values like DR Congo, Chad or Central Africa. There, inequality is often established by the social norms underlying the patriarchal society. Women marry early, do most of the family work, are less likely to be employed in a job with a contract and have limited political influence. For girls, school attendance is often significantly lower than for boys. Some countries with a high discrimination of women have a high HDI though. In Saudi Arabia for instance, the legal framework limits the rights of women. They need the permission of a guardian, which is mostly their husband, to travel, and sometimes even to work or to receive medical assistance.
Countries with a GDI of 0.925 to 0.950 are classified as having a medium discrimination of women. There are only few examples like Bolivia, Tanzania, Oman, and Indonesia.
About half of the countries have GDI values over 0.950 and a low or very low discrimination of women. They comprise nearly all states in the Americas, Europe, East Asia, Southern Africa and the Australasian region. There, women face similar job chances, wages, possibilities to politically participate and legal frameworks as men. Germany, for instance, has a value of 0.968. Nevertheless, the Gender Pay Gap is 21%, i.e. that women earn 21% less in jobs than men.
Currently, there are about 20 countries with GDI values over 1. The list comprises states like Qatar, Mongolia, Lithuania, Uruguay and the Philippines. So the places where the living conditions of females are better than those of men are widely spread on our planet, but do not follow a spatial pattern.
GDI and its practical application
The GDI can be used in development cooperation or state programmes. In developing countries with a low GDI, for instance, many projects focus on women, as they do most of the household and family work and thus are more responsible for the well-being of the people. Hereby, the idea is promoted that development can progress by a better integration and empowerment of women. Finally, the GDI can be also be used to assess the efforts made in the SDG 5 (sustainable development goal), which is gender equality.
GDI and its practical application
The GDI can be used in development cooperation or state programmes. In developing countries with a low GDI, for instance, many projects focus on women, as they do most of the household and family work and thus are more responsible for the well-being of the people. Hereby, the idea is promoted that development can progress by a better integration and empowerment of women. Finally, the GDI can be also be used to assess the efforts made in the SDG 5 (sustainable development goal), which is gender equality.